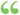 A sphere is a solid, bounded by one continued convex surface, every point of which is equally distant from a point within, called the centre. The sphere may be conceived to be formed by the revolution of a semicircle about its diameter, which remains... A sphere is a solid, bounded by one continued convex surface, every point of which is equally distant from a point within, called the centre. The sphere may be conceived to be formed by the revolution of a semicircle about its diameter, which remains...  A Treatise of Practical Mathematics - Page 192by Andrew Bell - 1842Full view A Treatise of Practical Mathematics - Page 192by Andrew Bell - 1842Full view - About this book
 | Joseph Harris - 1732 - 236 pages
...having every part of its Surface equally diftant from a Point within it, called its Center ; and it may be conceived to be formed by the Revolution of a Semicircle round its Diameter. Any Circle pafling through the Center of the Sphere, thereby dividing into two... | |
 | 1801 - 658 pages
...point of which is equally distant from a point within, call- LJL!| ed the centre. The sphere may -jj', be conceived to be formed by the revolution of a semicircle about its diameter, which remains fixed. 9. The axis of a solid is a line, drawn from the midd« of one end to the middle... | |
 | Samuel Webber - 1808 - 520 pages
...convex surface, every point of which is equally distant from a point within, called the centre* The sphere may be conceived to be formed by the revolution of a semicircle about its diameter, which remains fixed. 9. The axis of a solid, is aline drawn from the middle of one end to the middle... | |
 | Francis Nichols - 1811 - 162 pages
...contained under one uniform round surface, which is every where equally distant from a point within it called the centre. A sphere may be conceived to be...the revolution of a semicircle about its diameter, which remains unmoved, and is called the axis of the sphere. 2. A diameter of a sphere is a straight... | |
 | William Hawney - 1820 - 336 pages
...body, every part of its surface being equally distant from a point within, called its centre ; and it may be conceived to be formed by the revolution of a semicircle round its diameter. To find the Solidity. RULE I. Multiply the cube of the diameter by .5236, and the... | |
 | Rev. John Allen - 1822 - 516 pages
...sphere, is a right line drawn from the centre to any part of its surface. 16. When a sphere is supposed to be formed by the revolution of a semicircle about its diameter, which remains unmoved, the diameter, about which the semicircle revolves, is called, the axis of the... | |
 | Peter Nicholson - 1826 - 390 pages
...by the ends of the parallelogram are called the ends of the cylinder. A SPHERE, or GLOBE, is a solid formed by the revolution of a semi-circle about its diameter as an axis. A RING is a solid described by a circle revolving round a point without the circle, and in a direction... | |
 | Ireland commissioners of nat. educ - 1834 - 370 pages
...on. 9. A cone is a round pyramid, having a circle for its base. 10. A sphere is a round solid, which may be conceived to be formed by the revolution of a semi-circle about its diameter which remains fixed. 11. The axis of a solid is a line joining the middle* o> both ends. 12. When the... | |
 | James L. Connolly (mathematician.) - 1835 - 264 pages
...solid body, every part of whose surface is equally from a point within it, called the centre; and it may be conceived to be formed by the revolution of a semicircle round its diameter. To find its solidity, this is the RULE. Multiply the axis or diameter into the... | |
 | Commissioners of National Education in Ireland - 1837 - 290 pages
...on. 8. A cone is a round pyramid, having a circle for its base. 9. A sphere is a round solid, which may be conceived to be formed by the revolution of a semi-circle about its diameter which remains fixed. 10. The axis of a solid is a line joining the middle of both ends. 11. When the... | |
| |